Anemia or anemia is a condition that occurs when the number of red blood cells (red blood cells) in the body decreases or when the protein called hemoglobin falls below normal levels. Hemoglobin is a protein that transports oxygen in the blood through red blood cells. A decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood can cause insufficient oxygen to be transported to the tissues and impair cellular functions. This condition is called hypoxia and can affect many organs of the body.
If anemia is left untreated, it can lead to various problems in the body. The lack of oxygen to organs and tissues can lead to symptoms such as pain, emotional problems, forgetfulness and numbness in the hands and feet.
Anemia can occur due to different causes and has several types:
Iron deficiency anemia: When the body does not get enough iron, hemoglobin production decreases. This can be due to an iron-poor diet, blood loss or problems with the absorption of iron.
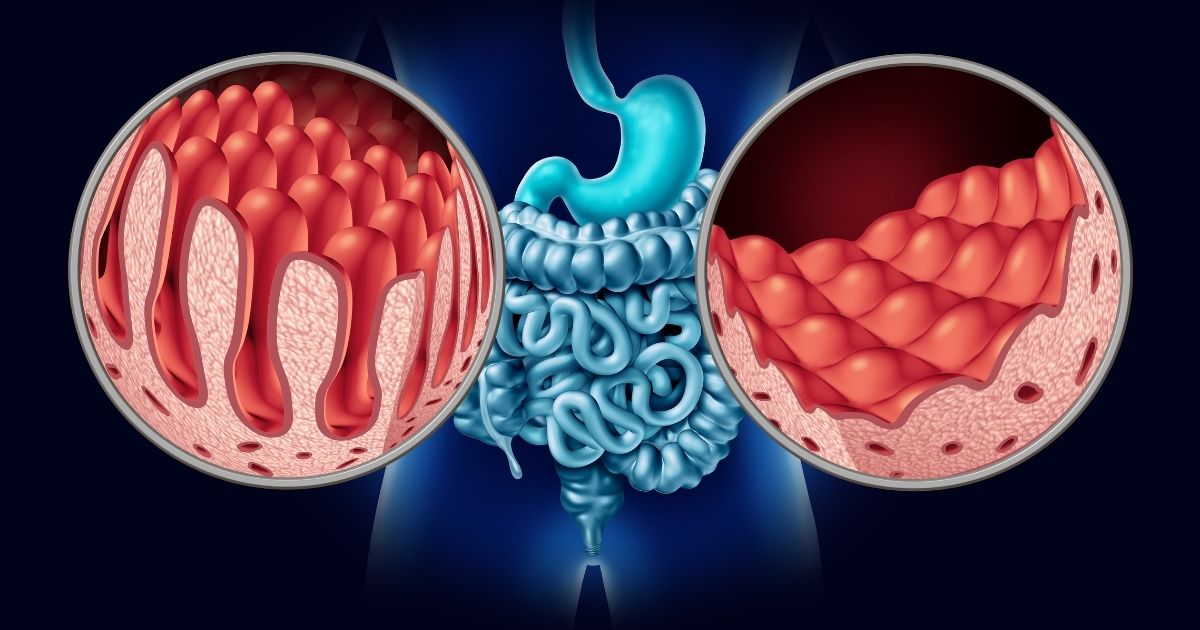
B12 Deficiency Anemia: This occurs when the body does not get enough vitamin B12. Vitamin B12 is essential for the production of red blood cells. This type of anemia can be caused by stomach diseases or nutritional deficiencies.
Folic Acid Deficiency Anemia: It occurs when the body does not get enough folic acid. Folic acid is important for red blood cell production. Inadequate consumption of green leafy vegetables or absorption problems can cause this type of anemia.
Sickle Cell Anemia: It is an inherited blood disorder. Red blood cells become sickle-shaped, which can cause blocked blood vessels.
Aplastic Anemia: Occurs as a result of bone marrow failure. Blood cells cannot be produced or are reduced.
Hemolytic Anemia: Red blood cells break down earlier than normal. It can be hereditary or develop as a result of infections or other factors.
Pernicious Anemia: Occurs as a result of vitamin B12 deficiency. Vitamin B12 cannot be absorbed due to the lack of a protein called intrinsic factor produced in the stomach.
Megaloblastic Anemia: Due to a deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid, red blood cells are produced in an abnormally large and immature form.
Symptoms of anemia may include weakness, paleness, dizziness, palpitations, hair loss. For diagnosis, your doctor may perform a physical examination and order blood tests. Depending on the cause of anemia, a treatment plan is determined. Dietary adjustments, iron or vitamin B12 supplements, medication or other treatment methods may be used. Anemia can be managed by identifying the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.