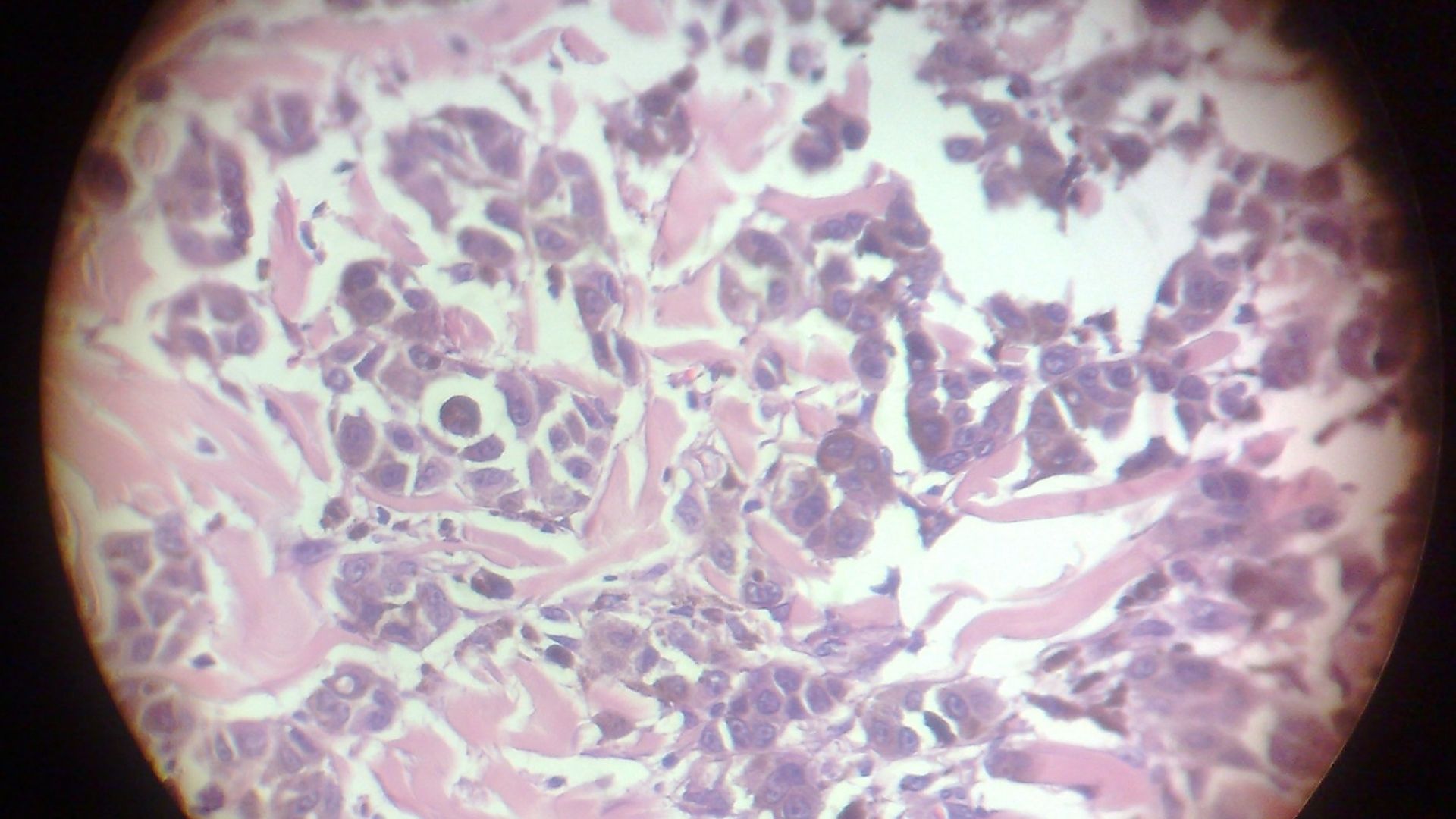
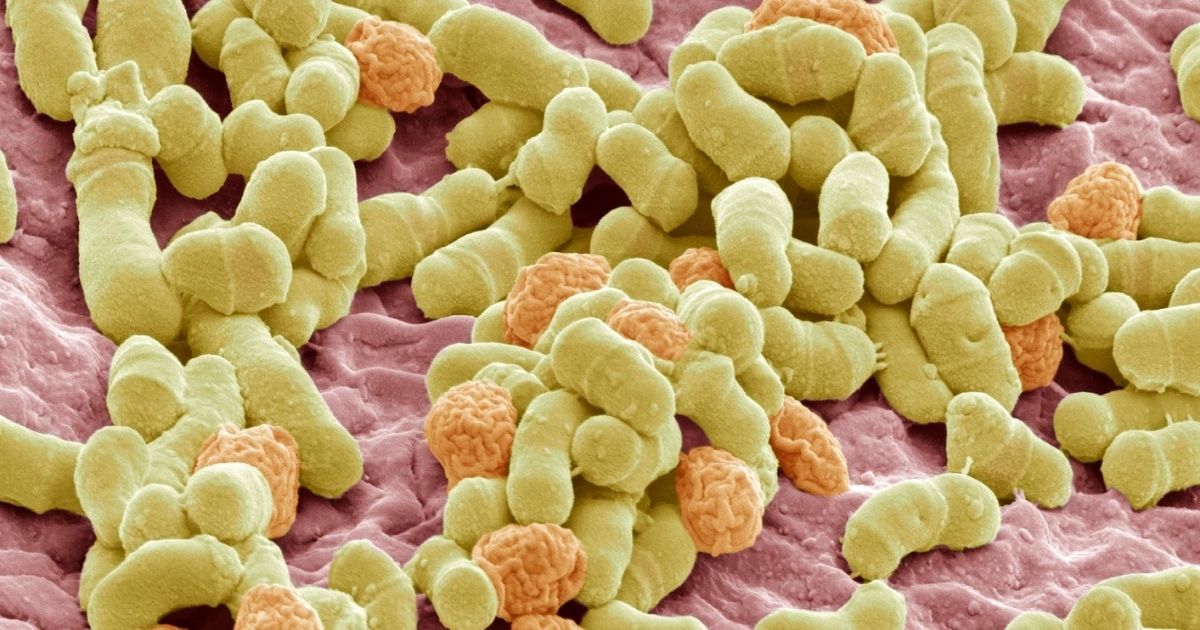
Impetigo is a contagious skin disease that occurs on the skin due to a bacterial infection. It usually occurs in children, especially children between 2 and 5 years old, but can occur at any age. Impetigo develops as a result of infections caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes.
Symptoms of impetigo include redness, blisters, fluid-filled sacs or vesicles, crusting, scabs, itching and sometimes mild fever. Impetigo usually appears on the face, lips, wings of the nose and hands, but it can also develop on other parts of the body. The infection becomes more contagious when the blisters burst or scabs form.
Impetigo can usually be diagnosed by clinical examination and evaluation of symptoms. However, in some cases, laboratory tests can be performed by taking a swab to determine the cause of the infection.
Treatment of impetigo usually involves local treatment methods and the use of antibiotics. It is recommended to keep infected areas clean and wash them regularly with antiseptic solutions. Topical antibiotic ointments are often used to treat impetigo. In cases of antibiotic-resistant conditions or widespread infections, oral antibiotics may be prescribed. It is important to use the medicines recommended by your doctor before starting treatment.
It is also important to take some precautions to prevent the spread of impetigo. Hygiene rules must be observed to avoid infecting other people by contact with infected areas. Hand washing, covering infected areas, not sharing personal items and cleaning and disinfecting the infected area frequently are important.
Impetigo is usually treatable and usually heals quickly. Starting treatment early reduces the spread of infection and the risk of complications. Following your doctor’s recommendations and taking the necessary precautions will speed up the healing process.