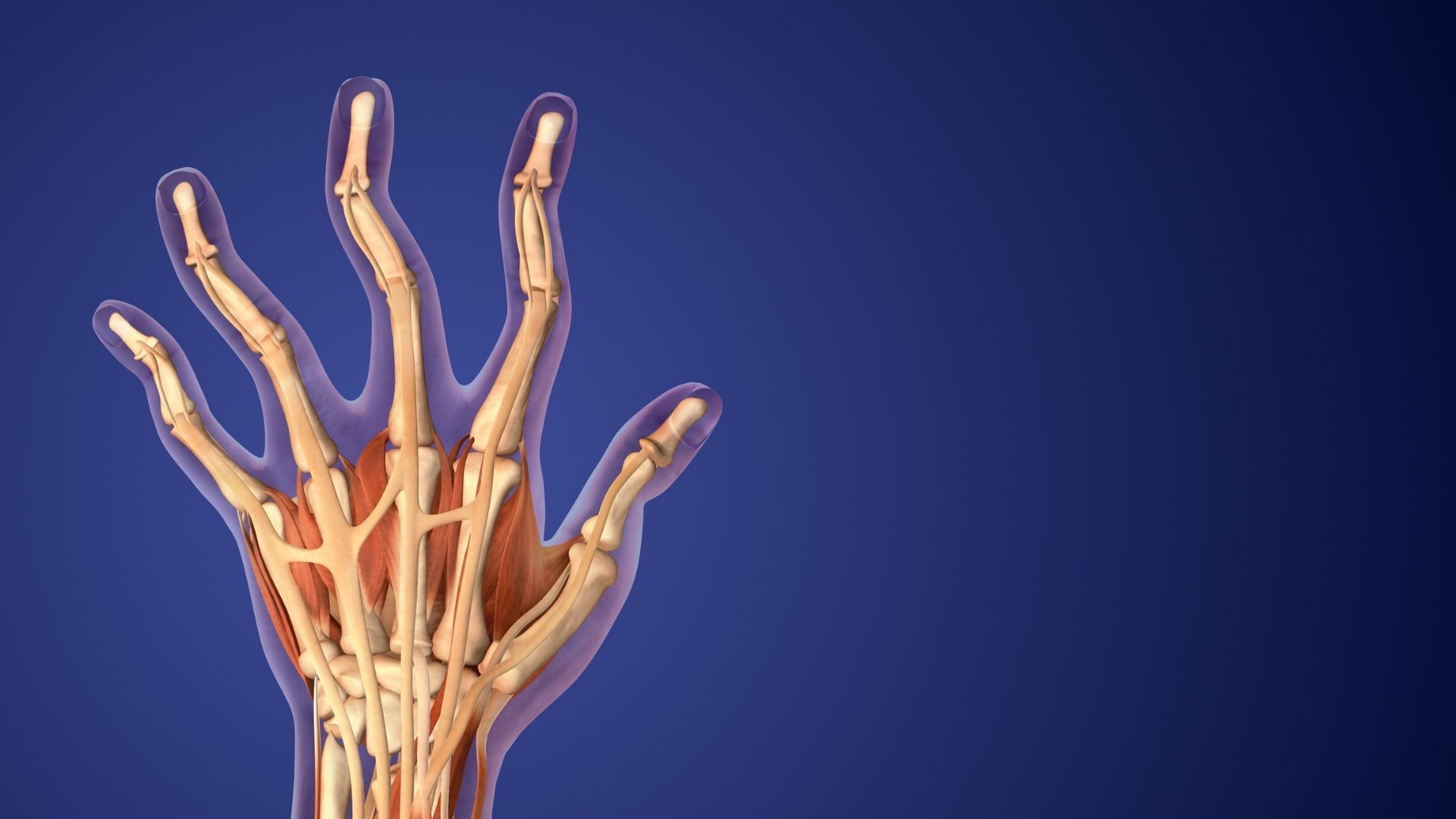
Rheumatoid arthritis, medically known as “inflammatory rheumatism”, is a chronic inflammatory disease. It is an autoimmune disorder that can damage body systems such as the skin, eyes, lungs, heart and blood vessels in some individuals. It is not a condition caused by extreme hot or cold weather. Rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, especially joint tissues.
This disease can lead to many systemic complications affecting the body. Modern drug treatment options have significantly improved outcomes, but severe rheumatoid arthritis can still trigger physical disabilities.
The cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not known exactly, but hereditary factors are thought to play a role. Genes, although not the direct cause of the disease, can make it more susceptible to environmental factors. Environmental factors, especially infections such as viruses and bacteria, can trigger the disease.
Factors that increase the risk of rheumatoid arthritis include gender, age, obesity, family history and smoking habits. Women in particular are more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis can occur at any age, but it is most common in middle age. There is also a special type of rheumatoid arthritis in children, which requires early diagnosis and treatment.
Pregnancy is an important consideration for people with rheumatoid arthritis. Pregnancy can be risky depending on the condition, the type of disease and the degree of internal organ damage. However, pregnancy may be possible under the supervision of a doctor and with careful follow-up.
Rheumatoid arthritis does not only cause joint problems. Other systemic complications include osteoporosis, rheumatoid nodules, dry eyes and mouth (Sjögren’s syndrome), infections, abnormal body composition, carpal tunnel syndrome, heart problems, lung disease, lymphoma and more.
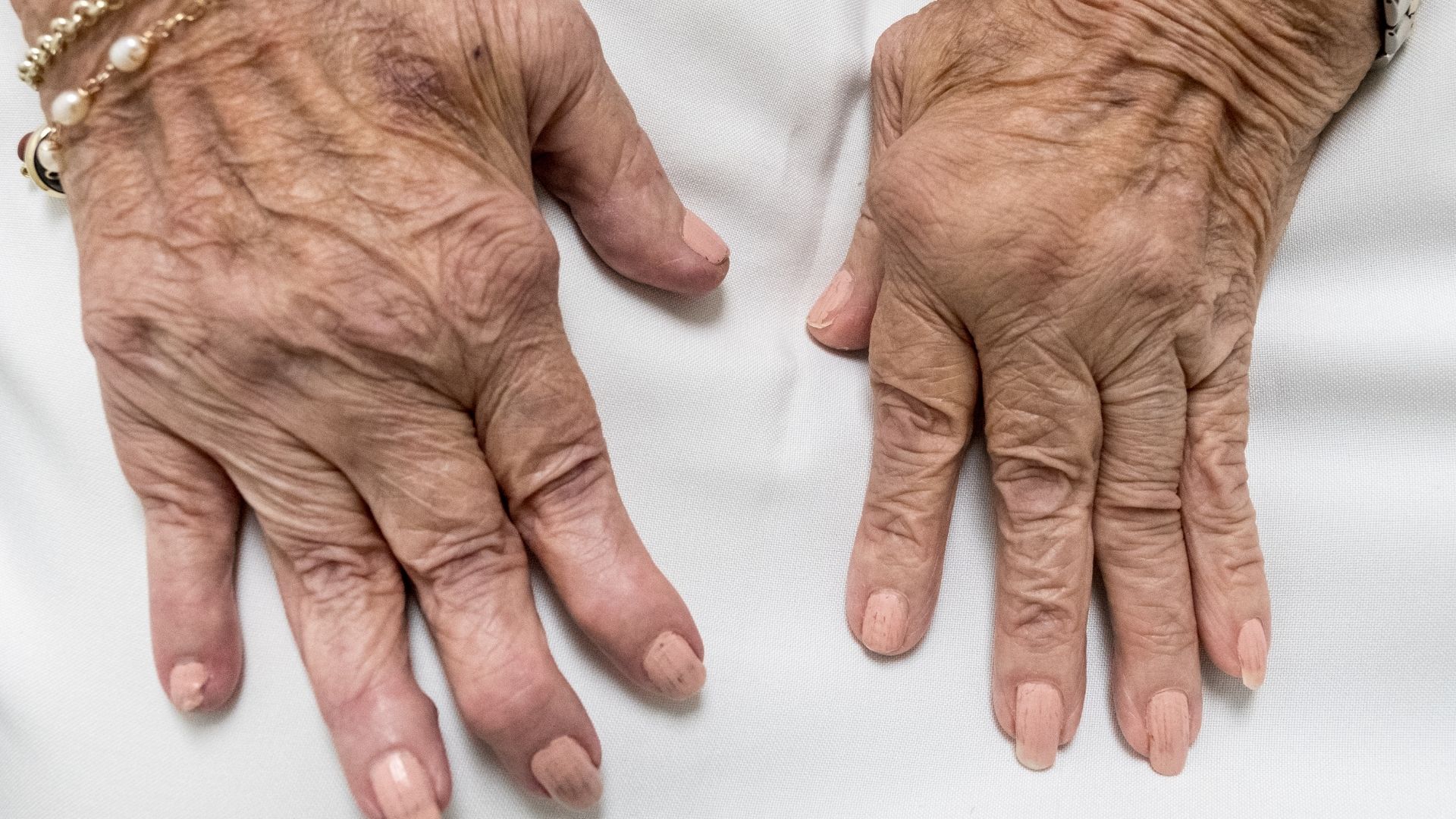
Symptoms include joints that feel tender, swollen and hot, joint stiffness in the morning and after long periods of inactivity, fatigue, fever and loss of appetite. While these signs and symptoms affect the joints, later stages of rheumatoid arthritis can also affect the lungs, kidneys, heart and other organs.
Rheumatoid arthritis is often difficult to diagnose in the early stages because its symptoms can be confused with those of other diseases. During a physical examination, the doctor examines the joints and looks for signs such as swelling, redness and warmth. Blood tests can help diagnose the disease by checking for erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, rheumatoid factor and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies.
Treatment may vary depending on the severity and duration of rheumatoid arthritis. Medication aims to slow the progression of the disease and relieve symptoms. Medications include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, DMARDs, corticosteroids and biological response modifiers. These medications can help prevent joint damage and relieve pain, but it is important to be aware of side effects.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation offers exercises and methods to restore joint flexibility and strength. Surgical intervention may be considered in cases that do not respond to medications and physical therapy. Surgical procedures such as joint fusion, synovectomy, tendon repair and total joint replacement may be used.
Individuals can relieve pain with lifestyle changes and home treatments. These changes can include exercise, weight control, rest, stress management and proper nutrition.
Untreated rheumatoid arthritis can lead to joint damage, loss of function and reduced quality of life.