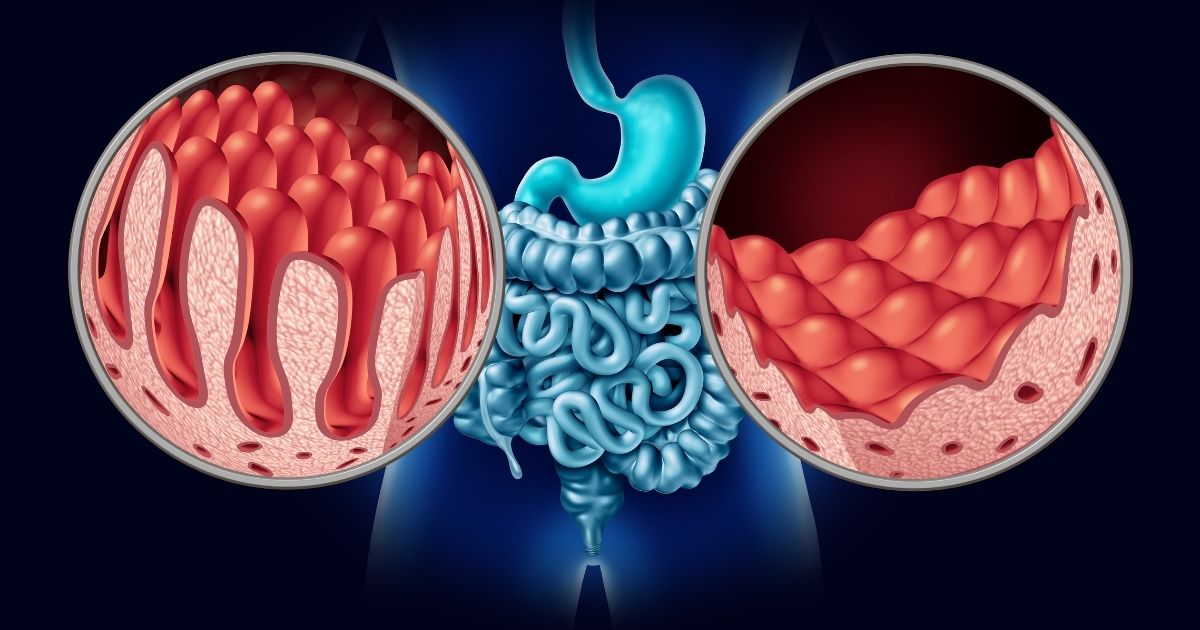
Celiac disease is a disease of the immune system caused by the body’s inability to tolerate gluten, a protein found in food. The disease is characterized by an overreaction of the body to the gluten protein found in wheat, barley and rye. Genetic factors play an important role in the development of the disease and a family history can increase the risk of celiac disease.
While the immune system normally protects the body against harmful substances, in celiac disease antibodies are mistakenly produced against the gluten protein. These antibodies cause damage to the small intestine and prevent nutrients from being digested and absorbed. In particular, the absorption of important nutrients such as iron and folic acid is impaired.
There are different types of celiac disease:
Classic Celiac: Usually occurs in young children. Symptoms include growth retardation, chronic diarrhea, abdominal distension, weakness, loss of appetite and vomiting.
Atypical Celiac: Usually occurs in older children and adults. Non-digestive symptoms may predominate, but digestive problems such as short stature, delayed puberty and tooth enamel problems may also occur.
Silent Celiac: Diagnosed incidentally during family screenings or tests for other reasons, without the person having any symptoms or signs.
Potential Celiac Disease: Positive results are obtained on celiac tests, but small bowel biopsies show normal or minimal changes. In this case, people are monitored regularly by a doctor.
Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity: People cannot tolerate gluten, but celiac disease-specific antibodies are not present and there is no damage to the small intestine. Diagnosis can be difficult and treatment may include a gluten-free diet.
The causes of celiac disease are related to genetic predisposition and family history is important. Genetically predisposed individuals develop symptoms when they consume foods containing gluten. This is why celiac disease is more common in areas where wheat is widely consumed and rare in areas where wheat is less commonly consumed.
Symptoms of celiac disease may vary according to age:
Children under 2 years of age: Symptoms such as vomiting, chronic diarrhea, abdominal distension, growth retardation and loss of appetite may be observed.
In Children Over 2 Years of Age and Adults: Symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, weight loss, anemia, fatigue, headache may occur. In adults, additional symptoms such as neurological symptoms, mood changes, skin rashes may also be observed.
Serologic tests and small bowel biopsy are used to diagnose celiac disease. Serologic tests are used to detect antibodies that indicate symptoms of the disease through blood tests. For a definitive diagnosis, a small bowel biopsy is performed, during which a tissue sample is taken from the intestine and examined for damage.
The only effective treatment for celiac disease is to completely eliminate gluten-containing foods from the diet. This gluten-free diet repairs the intestinal damage and makes the symptoms disappear. Patients should focus their diet on gluten-free foods such as corn, rice, soy, buckwheat. Supplements may also be needed to compensate for missing nutrients.